Wind Measurements
The wind brings us different sorts of weather. It also affects our lives when it blows strongly, and even when it does not blow. It is an important aspect of the weather for meteorologists.
When you have finished reading about this you may want to return to Collecting Data.
Wind MeasurementThere are two pieces of information that we need about the wind. We need to know
its direction and its strength. |
 |
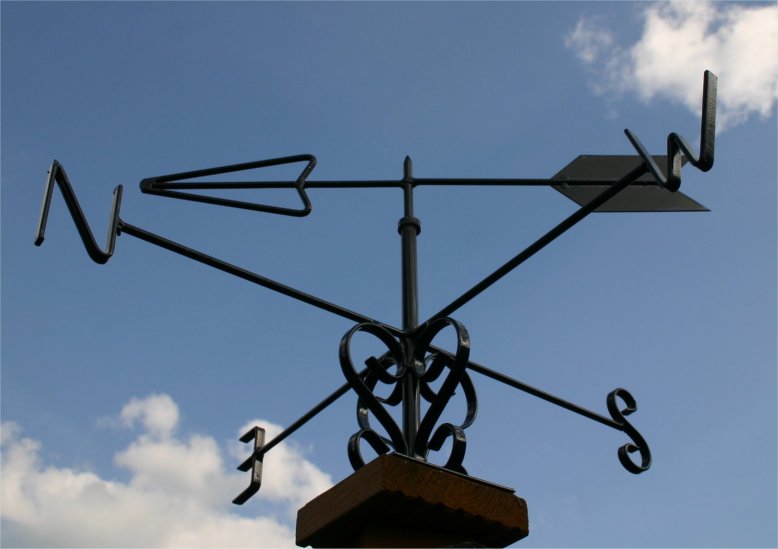
Wind DirectionThis is recorded by using the eight points of the compass. We record the direction
from which the wind is coming. This is important because different
directions will bring different types of weather. |
 |
Wind StrengthThis can be measured in kilometres per hour, miles per hour and metres per second (i.e. by measuring the speed of the wind.). It can also be measured by using the Beaufort Scale. The wind meter in the picture can be used to measure the strength of the wind in miles per hour, which can then be converted into Beaufort Scale measurements. |
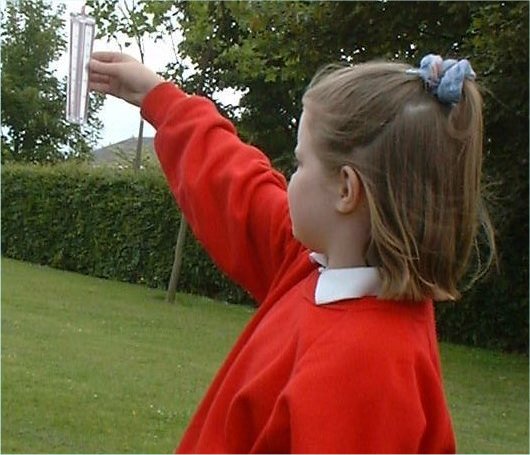 |
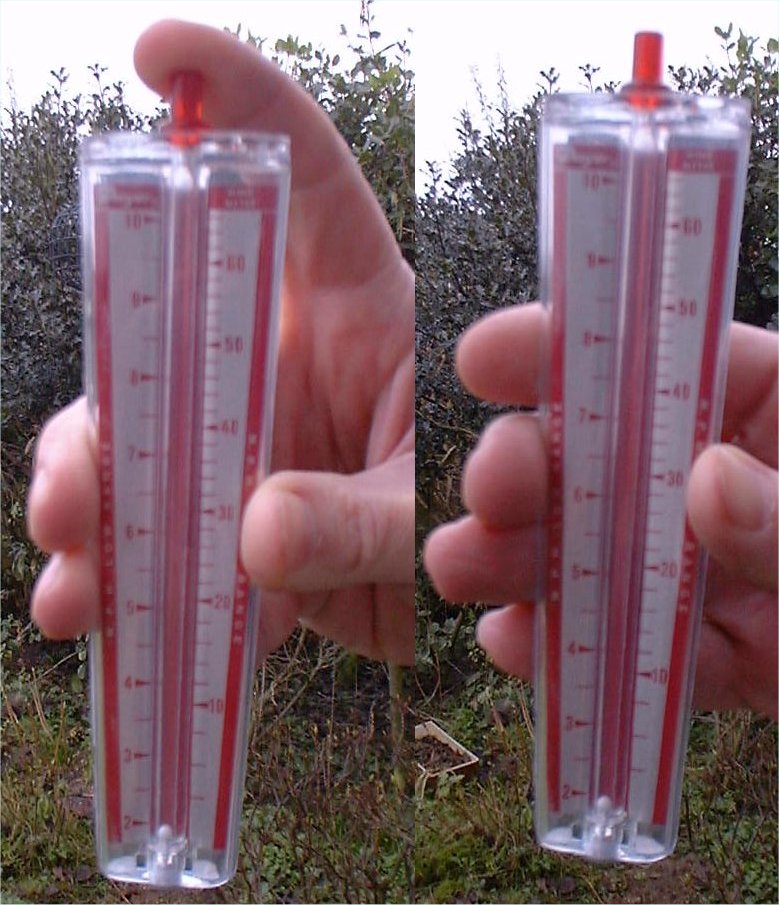
Wind Measuring DevicesThis instrument must be held in the middle, with the two holes at the bottom
facing into the strongest part of the wind. If there is wind,
the white ball in the central column will rise up. The monitor
needs to observe the rise and fall of this ball, and make a
judgment as to the average reading on the scale. If the wind
is gentle the aperture at the top is left uncovered, and the
left hand scale is read. If the wind is very strong the top
aperture is covered and the right-hand scale is used. |
 |
Using ICTThere are many digital devices which can help record the wind direction and strength. The advantage of the device in the photograph is that it can measure current wind strength, average wind strength and gusts. To see other digital devices look in the ICT page. |
 |
The Beaufort Scale
This scale helps people to describe how strong the wind is. There are numbers 0 to 12, with 0 being no wind, and 12 being the strongest. The pictures and descriptions below will help decide how strong the wind is. The scale was the work of Sir Francis Beaufort in 1805. His first descriptions helped sailing ships and had descriptions about the sea. It was later adapted for use on land. It is still used in shipping forecasts.
 |
|
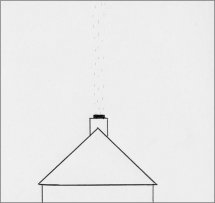
| 0 - Calm. Smoke rise vertically. (<1 kph) |
|
 |
 |
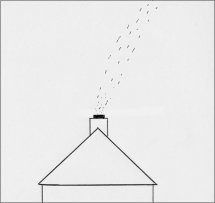
| 1 - Light Air. Smoke drifts. (1 - 5 kph) |
2 - Light Breeze. Wind felt on face. (6 - 11 kph) |
 |
 |
| 3 - Gentle Breeze. Leaves move. (12 -19 kph) |
4 - Moderate Breeze. Branches move. (20-28 kph) |
 |
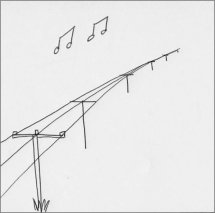 |
| 5 - Fresh Breeze - small trees sway. (29
- 38 kph) |
6 - Strong Breeze. Wires whistle. (39 - 49 kph) |
 |
 |
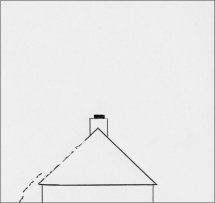
| 7 - Moderate Gale - whole trees sway. (50 - 61 kph) |
8 - Fresh Gale - twigs break off. (62 - 74 kph) |
 |
 |
| 9 - Strong Gale - slates are blown off.
(75 - 88kph) |
10 - Whole Gale - trees uprooted. |
 |
 |
| 11 - Storm - widespread damage. ( 103 - 117 kph) |
12 - Hurricane - disastrous. (over 117 kph) |